What is Corneal Cross-Linking?
Cross-linking is a minimally invasive procedure designed to halt the progression of keratoconus or corneal ectasia (weakened corneas due to refractive surgery).
In this treatment procedure, the cornea is strengthened using prescription eye drops along with UV light therapy. There might be several procedures tagged as cross-linking, but only one is FDA-approved. The FDA-approved cross-linking treatment procedure is performed with riboflavin-enriched eye drops –Photrexa® Viscous and Photrexa,® and the Glaukos KXL device.
How Does Corneal Cross-Linking Procedure Work?
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Glaukos Inc.’s corneal cross-linking system for progressive keratoconus in 2016. This is a novel, outpatient treatment procedure to treat keratoconus as well as the corneal thinning post-LASIK ectasia.
The cross-linking procedure takes approximately one hour. During the procedure, a riboflavin-enriched ophthalmic solution is placed on the eye and is then activated by UV light. This strengthens the collagen bonds within the cornea.
The cross-linking treatment can be done in two ways:
- Epithelium-off cross-linking: This technique is FDA-approved. In this treatment procedure, the epithelium on the cornea is removed before performing the cross-linking procedure.
- Epithelium-on cross-linking: This technique is currently undergoing FDA approval. In this technique, the epithelium is kept as it is, and the cross-linking procedure is performed.
Benefits of Corneal Cross-Linking Treatment
- Stiffens the cornea to help maintain its shape
- Shortens and thickens the collagen fibrils
- Creates new corneal collagen cross-links
What to Expect Before, During and After Corneal Cross-Linking Procedure
Before
The first step is a consultation visit to your eye doctor. The eye doctor will examine your eyes, diagnose your eye disorder, and discuss your treatment options. After determining whether the cross-linking procedure is right for you, the team will provide you with the pre-procedure guidelines.
During
- Corneal cross-linking is a simple, outpatient procedure.
- Anesthetic drops are placed on your eyes to numb them.
- The epithelium, a thin surface layer of the cornea, is removed.
- Photrexa Viscous eye drops are applied for approximately 30 minutes. If needed, Photrexa drops are used.
- After 30 minutes, Glaukos KXL light device is used to expose the corneas to UV light.
- At the end of the procedure, a special contact lens bandage is applied to your eye.
After
You must have a friend or family member to drive you back home after the procedure. It’s normal to experience mild discomfort and light sensitivity after the procedure. Your eye doctor will give your post-procedure guidelines and also schedule your follow-up appointments.
If you experience severe pain or sudden change in vision, or if your bandage comes off, contact your eye doctor right away.
Best Candidates for Corneal Cross-Linking Procedure
Corneal cross-linking is most effective when performed before keratoconus causes significant vision loss or before the cornea loses most of its shape.
If treated on time, cross-linking can halt the progression of keratoconus and improve the cornea’s shape, resulting in improved visual acuity.
Corneal cross-linking can also be performed in the following cases:
- Studies have found that corneal cross-linking can effectively eliminate a variety of corneal infections.
- Cross-linking treatment can be used in treating corneal ulcers that are unresponsive to topical antibiotics.
- People considering vision correction procedures such as LASIK can be pre-treated with cross-linking to strengthen the eye surface before undergoing the cornea reshaping procedure.
- Some surgeons have reported improved stability of the cornea in people who have undergone radial keratotomy (RK) and are experiencing daily fluctuations because of it.
What is Keratoconus?
Keratoconus also called as KC is an eye condition that results in progressive thinning of the cornea. In patients with keratoconus, the cornea, which is the clear outer layer of the eye, becomes thinner and weaker over time until it changes its shape –from a round dome to a cone-shaped bulge. Keratoconus usually develops in adolescence and gradually worsens.
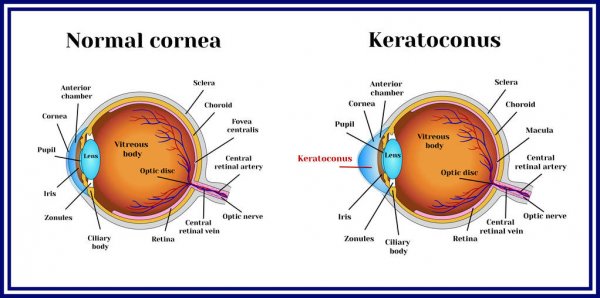
What Causes Keratoconus?
The exact reason of keratoconus is unknown; however, researchers have found that this eye condition could be linked to genetics and environmental allergies.
Keratoconus Symptoms
Keratoconus usually affects one eye at first and then progresses to the next one. This eye disorder changes the shape and the structure of the cornea and causes the following symptoms:
- Blurry vision
- Distorted vision
- Increased near-sightedness
- Sensitivity to light
Keratoconus affects the quality of life as it makes daily activities such as driving or reading, difficult or impossible. If the condition is left untreated, it can cause permanent vision loss.
Keratoconus Treatment Options
Until recently, patients suffering from keratoconus had no treatment options available. Corneal cross-linking is currently used to treat progressive keratoconus.
Contact Insight Vision Center for Corneal Cross-Linking Procedure
Insight Vision Center is equipped with Glaukos KXL system to treat keratoconus. The Glaukos KXL system is the new, cutting-edge device that allows eye doctors at Insight Vision Center to perform corneal collagen cross-linking, a newly FDA-approved treatment procedure for keratoconus.
If you need treatment for keratoconus or you have any questions about keratoconus or other vision problems, our qualified team of experts is here to help. Call us now.
Does insurance cover cross-linking?
Insurance coverage for FDA-approved cross-linking is now widely available as an increasing number of commercial insurance carriers are recognizing the medical necessity of the procedure. Greater than 95% of the commercially insured population has access to this potentially sight-protecting treatment.
For additional information on insurance coverage, visit the Cross-Linking & Insurance Guide
on LivingwithKeratoconus.com.

