Retinal Tear: Causes, Risk Factors, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
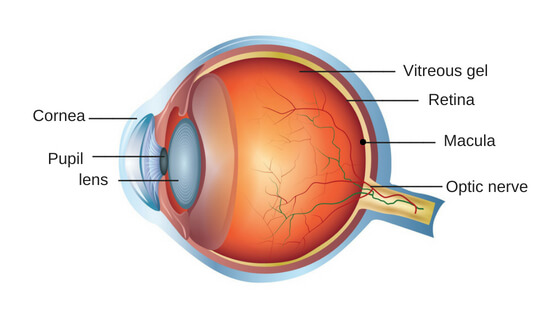
Do you know how you see the objects in front of you? Your retina generates your vision by passing on visual information to your brain via the optical nerve. The retina is a thin layer of tissue near the optic nerve connected to the inside of the eyes.
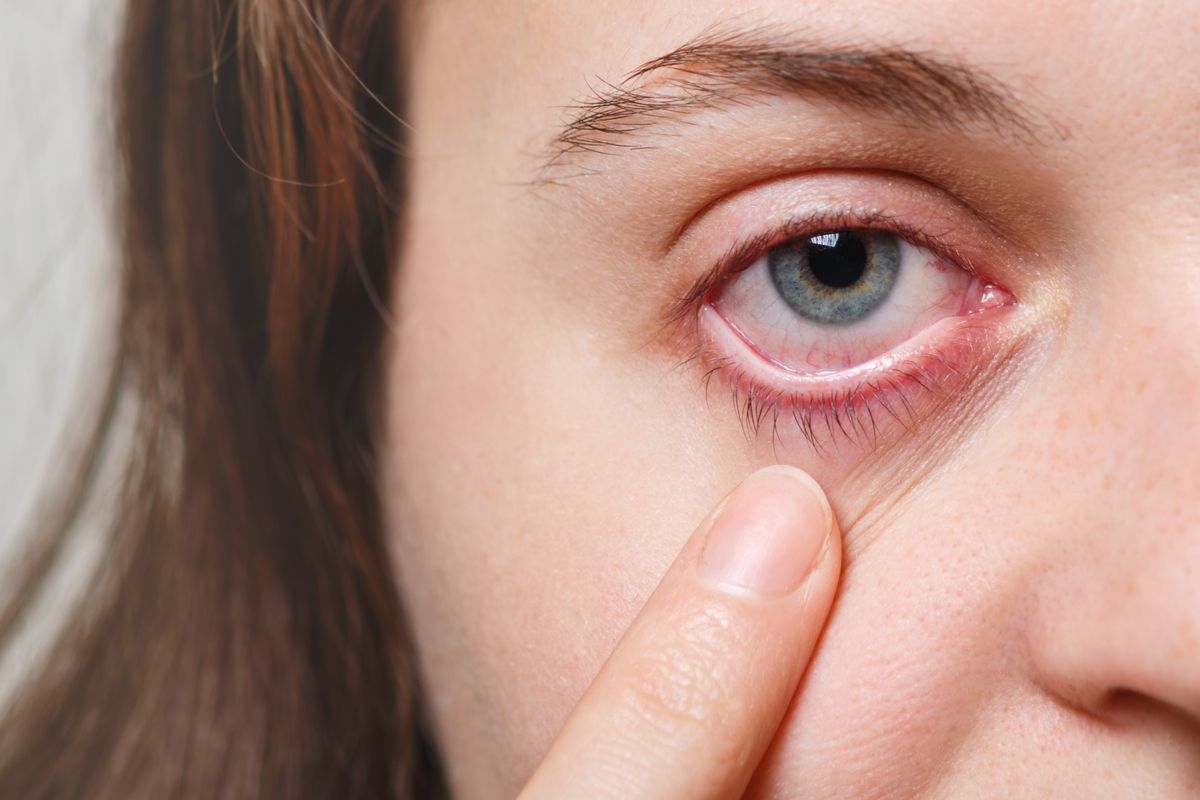
But sometimes, tears can be formed inside the retina, known as retinal tears. This scenario is risky as it can lead to a torn or detached retina and eventually vision loss.
This post contains information on the causes of a retinal tear, risk factors, retinal tear symptoms, diagnosis, and retinal tear treatment.
Continue reading Retinal Tear: Causes, Risk Factors, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment

Dr. Azhar I. Salahuddin is an ophthalmologist and is fellowship-trained in cornea, external diseases, and refractive surgery. Dr. Salahuddin has been performing cataract surgery for over 19 years and specializes ocular reconstruction, corneal transplantation surgery as well as vision correction through a variety of intraocular lenses. Dr. Salahuddin is board-certified by the American Board of Ophthalmology and was trained at Boston University.